# 一. 背景
# 1.单元测试的好处
- 单元测试不但会使你的工作完成得更轻松,大大减少你花在调试上面的时间
- 会令你的设计会变得更好,提高代码质量
- 减少bug,快速定位bug
- 放心地修改、重构
# 2.写单元测试要注意什么
- 不能只测试一条正确执行路径,要考虑到所有可能的情况
- 要确保所有测试都能够通过,避免间接损害
- 如果一个函数复杂到无法单测,那就说明模块的抽象有问题
# 3.单元测试的难点?
- 接口请求Mock代替真实网络请求
- 事件模拟
- UI测试
- react-hooks测试
# 4.为什么写单元测试?
为什么会拒绝单元测试?编写单元测试太花时间了?考虑下面问题:
- 对于所编写的代码,你在调试上面画了多少时间?
- 对于以前你自认为正确的代码,而实际上这些代码却存在重大的bug,花了大量时间重新确认这些代码?
- 对于一个别人报告的bug,你花了多少时间才找出导致这个bug的源码位置?
# 二. 调试工具
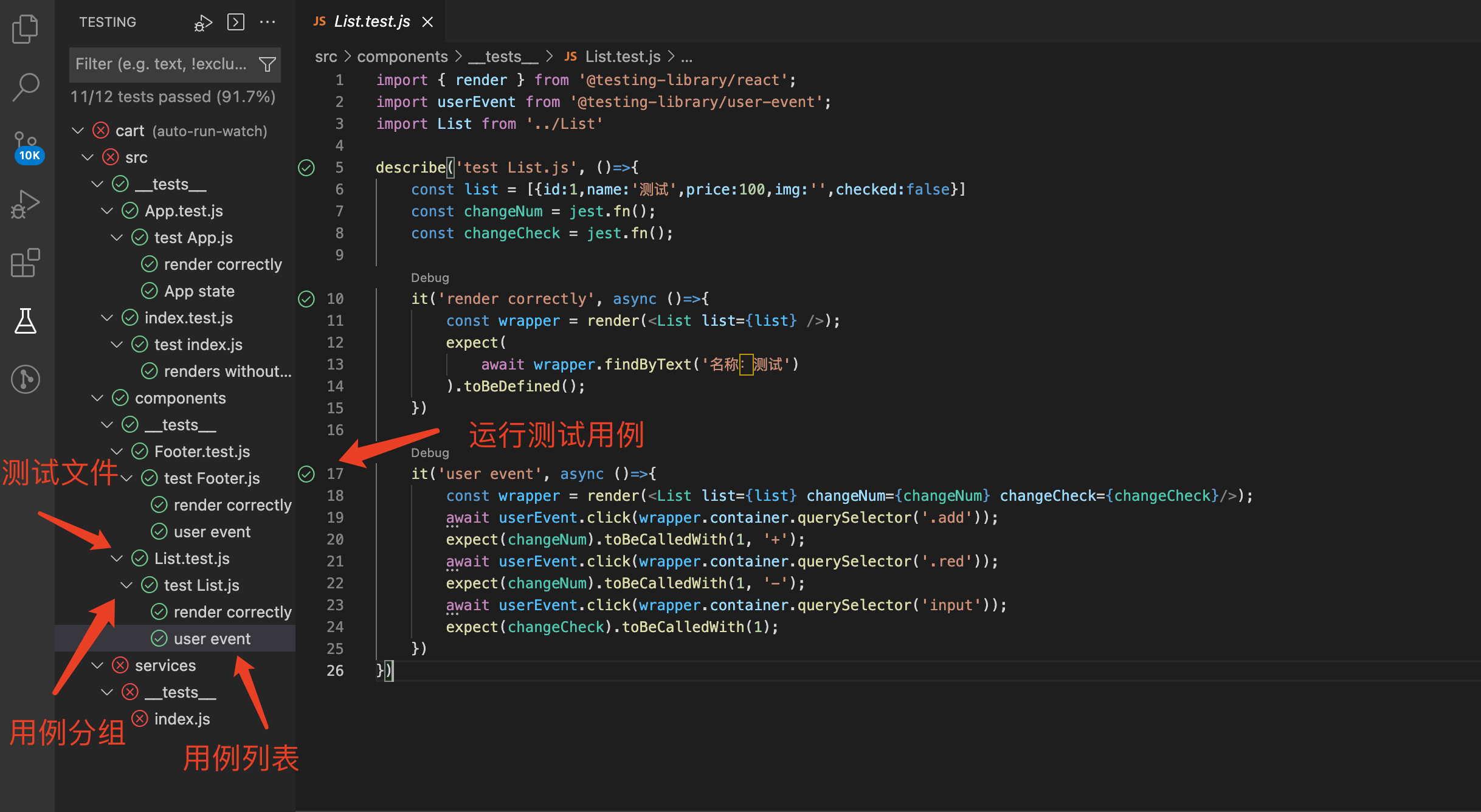
# 1. 整个工程运行单测
// 运行测试
npm run test
// 显示覆盖率,分为statements、branch、functions、lines
npm run test --coverage
// Version Control Integration
npm run test => a
# 2. 单个文件运行单测
npm run test '/Users/mj/web/cart/src/__tests__/index.test.js'
# 3. 安装 jest 插件
# 三. 基础语法
将编写单测过程中经常涉及的用法处理罗列。
# 1. 比较
全等
const obj = {};
expect('123').toBe('123');
expect(obj).toBe(obj);
结构相等
const obj = {a:1,b:2};
expect(obj).toEqual({a:1,b:2});
字符串模糊匹配
const someString = 'hello123 world'
expect(someString).toEqual(expect.stringContaining(`ell`));
对象拥有属性
const obj = {id:'123'};
expect(obj).toHaveProperty('id');
expect(obj).not.toHaveProperty('id');
对象结构模糊匹配
const obj = {show(){},name:'xxx',address:'xxx北京yyy'};
expect(obj).toMatchObject({
show: expect.any(Function),
name:'xxx',
address:expect.stringContaining('北京')
});
# 2. 模拟、附加
jest.mock 将整个目标模块对应的函数属性包装为 jest 函数,以便断言 可以结合 mocks/moduleName.js 使用 (有该文件存在则优先加载该模块)
jest.mock('moduleName');
将模块替换为指定内容
jest.mock('moduleName',()=>({a:1,b:jest.fn()}));
jest.spyOn 附加 spy 翻译 间谍,用于将原始对象的函数替换为 jest 包装后的函数,使之可断言
const obj = {someFunction(){console.log('hello')}};
jest.spyOn(obj,'someFunction');
expect(obj.someFunction).toHaveBeenCalled();
jest.mockImplementation 对已经被 jest 包装后的函数临时或者永久替换
// someFunction 必须被模拟或者附加
const someFunction = jest.fn();
someFunction.mockImplementationOnce(()=>{console.log('only once')});
someFunction.mockImplementation(()=>{console.log('every times')});
// 撤消上述的 mock 实现
someFunction.mockReset();
# 3. 异步处理
模拟异步函数的结果
const mocks = {
axios: {
get: jest.fn()
}
};
// 对异步函数模拟预期返回值
mocks.axios.get.mockRejectedValue('error');
await expect(mocks.axios.get).rejects.toEqual('error');
mocks.axios.get.mockResolvedValue('success');
await expect(mocks.axios.get()).resolves.toEqual('success');
// 异步抛出异常
const error = new Error('error');
mocks.axios.get.mockRejectedValueOnce(error);
await expect(mocks.axios.get).rejects.toThrow(error);
# 4. 异常处理
捕获错误
const someFunction = ()=>{ throw new Error('xyz unkow error abcedfg')}
// 直接抛出异常的函数会导致 jest 中止,使用箭头函数包装一层传递给 expect 捕获错误
// 抛出具体错误信息
expect(() => someFunction()).toThrow('xyz unkow error abcedfg');
// 抛出过错误
expect(() => someFunction()).toThrow();
// 模糊匹配抛出的错误信息
expect(() => someFunction()).toThrow(
expect.objectContaining({
message: expect.stringContaining('error')
})
);
# 5. 函数调用
函数调用过
const someFunction = jest.fn();
someFunction();
expect(someFunction).toHaveBeenCalled();
expect(someFunction).not.toHaveBeenCalled();
函数调用次数及参数
const someFunction=jest.fn(()=>{});
someFunction('a');
someFunction('b');
// jest 包装后的函数可以调出 mock.calls 属性,它是一个数组其长度代表被调用的次数
// 数组每一个元素也是一个数组,值为该函数调用时数组化后 arguments
expect(someFunction.mock.calls.length).toBe(2);
expect(someFunction.mock.calls[0][0]).toBe('a');
expect(someFunction.mock.calls[1][0]).toBe('b');
函数调用参数模糊判断
const someFunction=jest.fn(()=>{});
someFunction('hello123','world');
expect(someFunction).toHaveBeenCalledWith(
expect.stringContaining(`ell`), 'world'
);
# 四. 项目中实战
# 1. 涉及工具介绍
# 2. 业务工程结构分析
专注业务逻辑本身而不是依赖的逻辑
# 不需要单测的文件
- 配置文件
- constants/*.js
- config/
- locale/*.js
- *.env
- 固定结构文件
- services/*.js
- mocks/*.js
- routes.js
# 需要单测的文件
- 状态管理
- stores
- reducers
- 视图组件
- jsx
- api视图组件
- 纯js业务逻辑
- app.js
- utils
- hooks
- others
# 3. 项目配置
/*
* For a detailed explanation regarding each configuration property, visit:
* https://jestjs.io/docs/configuration
*/
const path = require('path');
module.exports = {
// The directory where Jest should store its cached dependency information
// cacheDirectory: "/private/var/folders/_t/rxp8v70x2_lbqd6nqg981vph0000gn/T/jest_dx",
// Automatically clear mock calls, instances and results before every test
clearMocks: true,
// Indicates whether the coverage information should be collected while executing the test
collectCoverage: true,
// An array of glob patterns indicating a set of files for which coverage information should be collected
// collectCoverageFrom: undefined,
// The directory where Jest should output its coverage files
coverageDirectory: "coverage",
// An array of regexp pattern strings used to skip coverage collection
// coveragePathIgnorePatterns: [
// "/node_modules/"
// ],
// Indicates which provider should be used to instrument code for coverage
// coverageProvider: "babel",
// A list of reporter names that Jest uses when writing coverage reports
coverageReporters: [
"json",
"text",
"lcov",
"clover"
],
// An object that configures minimum threshold enforcement for coverage results
// coverageThreshold: undefined,
// The maximum amount of workers used to run your tests. Can be specified as % or a number. E.g. maxWorkers: 10% will use 10% of your CPU amount + 1 as the maximum worker number. maxWorkers: 2 will use a maximum of 2 workers.
// maxWorkers: "50%",
// An array of directory names to be searched recursively up from the requiring module's location
// moduleDirectories: [
// "node_modules"
// ],
// An array of file extensions your modules use
moduleFileExtensions: [
"js",
"jsx",
"ts",
"tsx",
"json",
],
// The root directory that Jest should scan for tests and modules within
rootDir: path.resolve(__dirname),
// A list of paths to directories that Jest should use to search for files in
roots: [
"<rootDir>"
],
// The paths to modules that run some code to configure or set up the testing environment before each test
// setupFiles: [],
// A list of paths to modules that run some code to configure or set up the testing framework before each test
setupFilesAfterEnv: ["<rootDir>/src/setupTests.js"],
// The number of seconds after which a test is considered as slow and reported as such in the results.
// slowTestThreshold: 5,
// A list of paths to snapshot serializer modules Jest should use for snapshot testing
// snapshotSerializers: [],
// The test environment that will be used for testing
testEnvironment: "jsdom",
// The glob patterns Jest uses to detect test files
testMatch: [
"**/__tests__/**/*.[jt]s?(x)",
"**/?(*.)+(spec|test).[tj]s?(x)"
],
// An array of regexp pattern strings that are matched against all test paths, matched tests are skipped
testPathIgnorePatterns: [
"/node_modules/",
'!**/__demo__/**',
'!**/__mocks__/**',
'!**/mock/**',
'!**/config/**',
'!**/constants/**',
'!**/services/**',
'!**/router/**'
],
// This option sets the URL for the jsdom environment. It is reflected in properties such as location.href
// testURL: "http://localhost",
// An array of regexp pattern strings that are matched against all source file paths, matched files will skip transformation
// transformIgnorePatterns: [
// "/node_modules/",
// "\\.pnp\\.[^\\/]+$"
// ]
};
# 4. js版本简易购物车
代码仓库:cart
# branchs
- main: js版本示例
- rtl: js+单元测试
# 5. 补全测试代码
- 普通函数
- UI视图
- 组件
- Hooks